Volume 1 (2017) – 33 articles
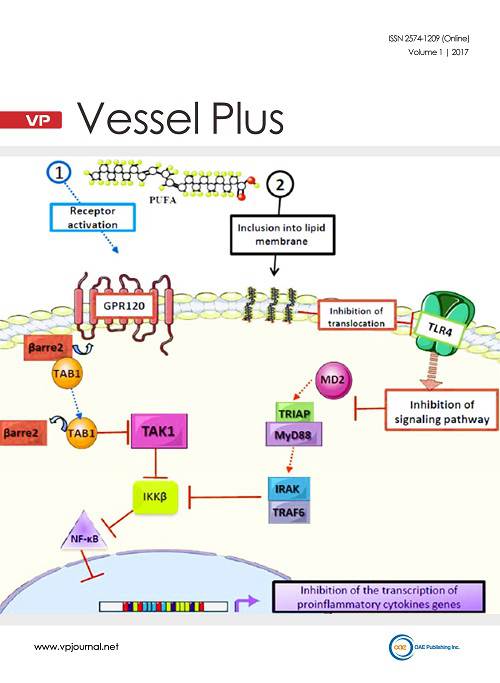
Cover Picture: Role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in proinflammatory cytokine synthesis. EPA and DHA inhibit the production of proinflammatory cytokines through different mechanisms: (1) binding of EPA and DHA to the G protein-coupled receptor (GPR120) leads to its activation and binding to β arrestin-2, which then dissociates into TAB1 and inhibits TAK1, thus interrupting the IKKβ/NF-κB cascade; (2) the inclusion of EPA and DHA into the lipid bilayer, which modifies lipid rafts and interrupts the translocation of TLR-4 and the MD2/TRIAP-MyD88/IRAK-TRAF6/IKKβ/NF-κB pathway, thus inhibiting the production of cytokines, showing the antiinflammatory action of EPA and DHA.
view this paper
Read Online Viewed:
Download This Volume Viewed:







