Volume 4 (2020) – 42 articles
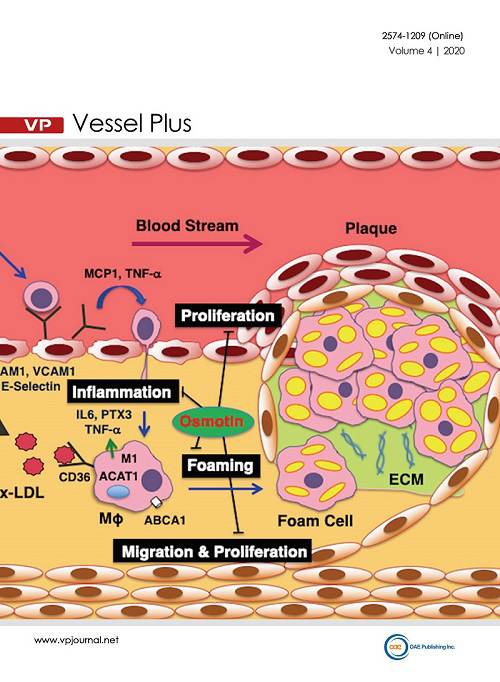
Cover Picture: Osmotin, a natural plant protein found in tomato, potato, pepper, and tobacco, is a homolog of human adiponectin. It exerts multiple biological activities through adiponectin receptors in a variety of mammalian cells. The therapeutic properties of osmotin have recently been shown in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis by in vitro and in vivo experiments. Osmotin suppresses the adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells by downregulating inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules in both cells. It suppresses oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced foam cell formation by downregulating cluster of differentiation 36 and acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase 1 as well as upregulating ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 in monocyte-derived macrophages. In vascular smooth muscle cells, osmotin suppresses the migration, proliferation, and production of collagen 1, fibronectin, and matrix metalloproteinase 2 by decreasing the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2 and nuclear factor-κB as well as increasing AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) expression. Treatment with osmotin suppresses abdominal fat accumulation in C57BL/6 mice and prevents the development of aortic atherosclerotic lesions, improving vascular inflammation and plaque instability in apolipoprotein E-deficient (Apoe-/-) mice. Osmotin protects against obesity- and diabetes-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in leptin-deficient obese (ob/ob) and leptin receptor-deficient diabetic (db/db) mice. These effects are attributed to the stimulatory actions of osmotin on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α and AMPK. Moreover, osmotin lowers serum levels of total cholesterol and triglyceride in non-diabetic and diabetic rats. These findings suggest that osmotin contributes to improving the extracellular risk factors for atherosclerosis and vascular intracellular and molecular responses. Therefore, the novel phytochemical osmotin may serve as a novel therapeutic target for atherosclerosis and related diseases.
view this paper
Read Online Viewed:
Download This Volume Viewed:







